托福高频考点之地质地理
作者:夏双双 武汉新航道北美考试院托福讲师
新托福考试中,不管是听力还是阅读,地质学geology都是高频考点,今天我们就一起来看一下托福考试中常考的地质学背景知识。
Lithosphere岩石圈
地球的岩石圈为我们直接提供了栖息地habitat,而其地质活动也对人类的生存产生了重要的影响。
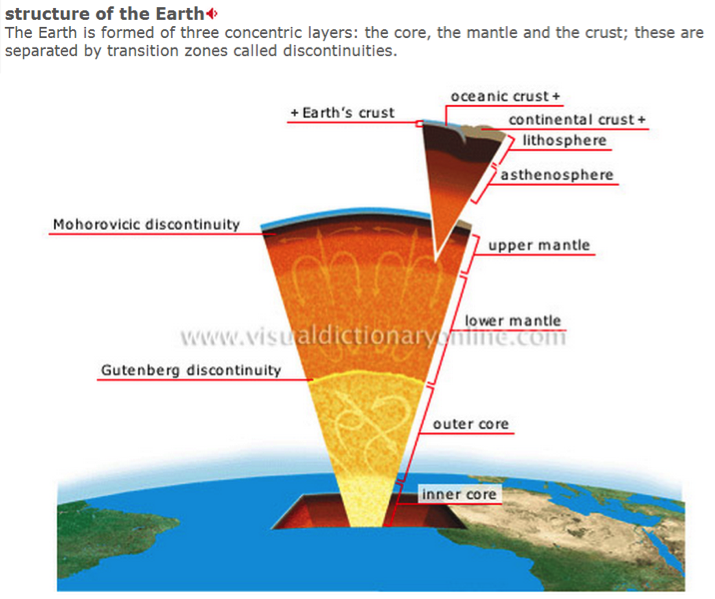
地球的岩石圈由 最外层的坚硬地壳 以及上层地幔构成。Earth's lithosphere includes the crust and the uppermost mantle, which constitute the hard and rigid outer layer of the Earth.
地球岩石圈被我们的构造板块分开的。The lithosphere is subdivided into tectonic plates构造板块. 而我们的板块plate/slab是躺着我们的下层的流动地幔上到的 lay on the liquid mantle地幔/molten rock,因此形成了板块漂移plate drift。
学科词汇
lithosphere岩石圈
crust 地壳
continental crust vs oceanic crust
mantle/molten rock地幔 --dismantle 揭露
plate tectonics板块构造
plate drift 大陆漂移
collide 碰撞
boundary 交界处
subduction zone 俯冲带
divergent/convergent plate boundaries
参见
TPO31L2plate drift
TPO7Reading 1

新托福考试中最常提及的两种基本的剧烈的地质活动There are 2 basic forms of violent geological activities: volcanic activities 火山活动& seismic activities 地震活动。并且两者是相互影响的。
通常认为两板块交界处易发这种剧烈的地质活动Boundaries between two plates/slabs are more prone to volcanic activities & seismic activities,也就是 板块构造学说plate tectonics。
但是有的时候板块中央也易发火山活动,甚至形成整条的火山链volcanic chain, 比如说夏威夷岛链 Hawaii island chain。这种不典型的火山称之为Volcanic anomaly 火山变体,关于其成因主要有两个theories
Theory1: plume theory岩浆柱理论
hot spots exist below tectonic plate when a column of extreme hot magma built up from deep inside of the planet’s core and melt through earth’s crust
Theory 2:Crack hypothesis裂缝理论
hot spots are created when a piece of the crust gets stretched increasing thinner and formed small cracks through which magma just beneath the surface crust pushes up to form volcanoes.
托福中有的时候还会考火山活动的影响,譬如火山喷发会释放大量的二氧化硫sulfur dioxide 以及火山灰ash, 影响局部甚至全球的气候;活火山附近还会出现一种非常罕见的非连续性喷泉a rare intermittent spring/fountain,即间歇泉, 主要由地下附近岩浆堆积导致build-up of proximate magma.
学科词汇
crater 火山口
dormant volcano休眠火山; active volcano 活火山;extinct volcano 死火山
geyser间歇泉
volcanic ash 火山灰 ash/soot/dust
magma/molten rock 岩浆
lava 火山所喷出的熔岩 vs larva 幼虫
粘稠度viscosity从高到低
tholoide/belonite volcano钟形火山
circular cone volcano 圆柱形火山
shield volcano 盾形火山
volcanic anomaly 火山变体
hot spot (火山)热点
plume hypothesis岩浆柱理论 Plume 岩浆柱
crack hypothesis裂缝理论
crack/split/fissure/ crevasse/ crevice/gap/edge/frontier裂缝同义词必须有听辩!
参见
TPO48L2 volcanic anomaly
TPO24L4 shield volcano on Venus
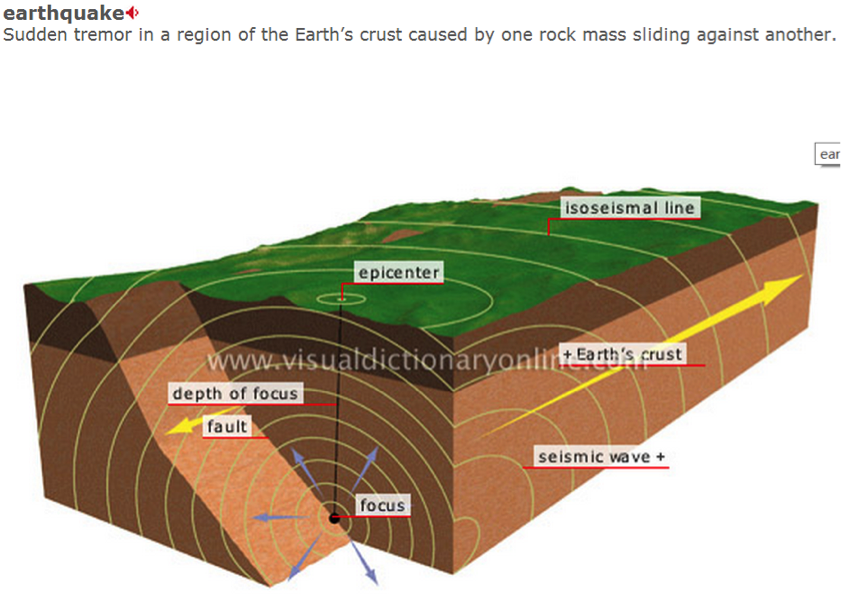
地震活动seismic activities作为另一总常考的地质活动,不管在阅读还是听力中,其学科词汇也体现了一定难度,譬如fault的意思不再是“错误”,而是“断层”。希望大家不仅做到认得这些学科词汇,同时能保证发音正确,有基本的听辨。例如TPO7Reading 1就提到2000万年前地中海以前是通过两条狭窄的海峡two narrow straits连通大西洋的,但由于地壳的运动crustal movement,海峡闭合, 逐渐形成了沙漠;然后在550万年前,由于地壳调整crust adjustment和断层作用faulting, 现在链接地中海和大西洋的直布罗陀海峡the strait of Gibraltar又打开了。
学科词汇
fault 断层;错误
seismic 地震的
seismology 地震学
seismograph 地震仪
tsunami 海啸 跟earthquake地震 都属于 seismic activity
bend and fold the soil
参见
TPO7reading 1
老托52 earthquake tilt fault
老托 15 earth’ structure
老托49 re-calculate the elevation of Mount Everest
老托 52 earthquake tilt fault
听力真经11-13 open pit
听力真经08-09 fault line
人类开发最广的岩石圈里还给我们提供了非常多的资源,包括各种矿石ore,含水土层aquifer中的地下水underground water。
顾名思义,含水土层定义为具有透水性permeable,含水的water-bearing,地下岩石underground layer of rock,水在这里面可以轻松地流动flow,包括巨石 boulder,破裂的石灰岩limestone,gravel,砂岩sandstone;可以是松散的沙子loose collection of sand,也可以是silt 淤泥。根据其中的水是否在自然状态下参与水循环,可将其分为unconfined aquifer 非承压含水层vs confined aquifer承压含水层。

学科词汇
pedosphere 土壤圈
aquifer含水土层
water table 地下水位 the level below the surface of the ground where water can be found
saturated 饱和的 unsaturated 不饱和的
permeable透水性的 permeability 透水性
water flow水流
boulder巨石
gravel砂砾,碎石
sandstone砂岩
ore矿石[ɔr](单音节反而是听力中的听辩难点!)
calcite方解石; gypsum;limestone石灰石; quartz 石英;crystal水晶;
sedimentary rock沉积岩
sediment→(weather风化, transfer转移 &deposit沉积)→sediment沉积物→(lithification石化作用)
igneous rock火成岩
granite花岗岩; obsidian黑曜石
metamorphic rock变质岩
marble大理石、limestone 石灰石
参加TPO16L1 Lechuguilla cave
TPO3 Reading 2 depletion of the aquifer
TPO21Reading 1 the formation of geothermal energy
Topography地形学
地形学经常以inter-disciplinary approach跨学科发的形式出现,譬如地形与气候的相互影响,所以基本的概念还是要能够认得跟听辩的!
inter-disciplinary approach跨学科方法
topography 地形 topographic feature 地形特点/地貌
sloping terrain倾斜的地貌
A land mass 大陆块is a very large area of land such as a continent
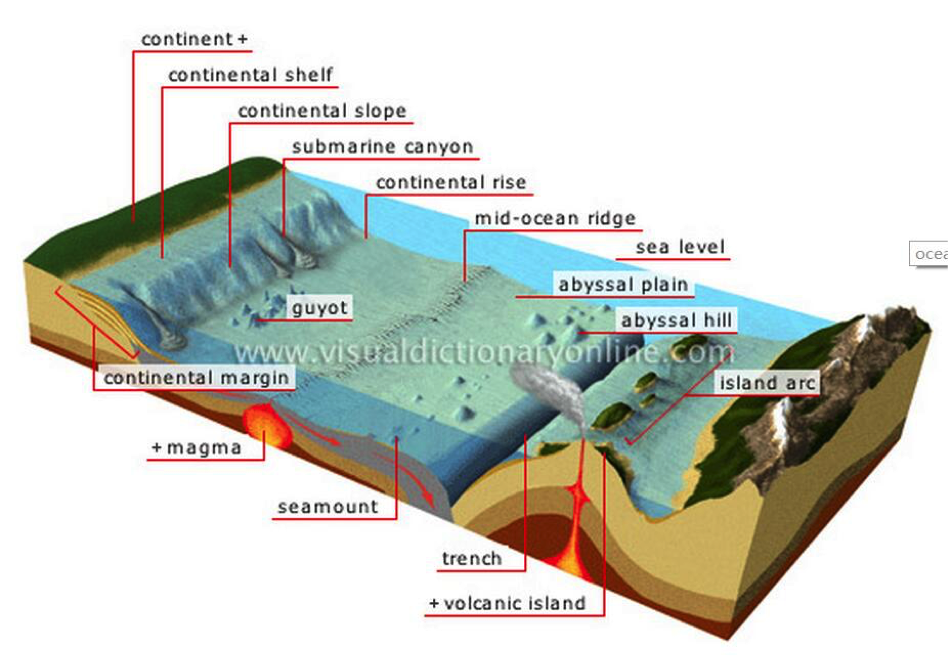
continent 大陆
continental shelf 大陆架
an underwater landmass which extends from a continent, resulting in an area of relatively shallow water known as a shelf sea
continental slope 大陆坡
(严格意义上,两者均为大陆一部分,但是在海平面下)
Slope 斜率 (steep/gentle); 斜坡 --ramp
Sea Level 海平面 altitude/elevation海拔
shelf /shallow sea 浅海区域
abyssal region 深海区域 Abyssal 深渊 Abyssal plain深海平原
basin 盆地,流域
The basin流域 of a large river is the area of land around it from which streams run down into it such as the Amazon basin亚马孙流域
sea floor海床 river bed 河床 upstream 上游 downstream 下游
Nile valley [naɪl]
plateau [plæ'to]高原
Mt Everest珠穆朗玛峰
Sahara [sə'hɑ:rə; -'heə-] desert撒哈拉沙漠
ranch牧场 prairie大草原 savanna [sə'vænə] 热带草原;热带的稀树大草原
meadow /Pasture 草原 vs pastor 牧师 pastoral田园的
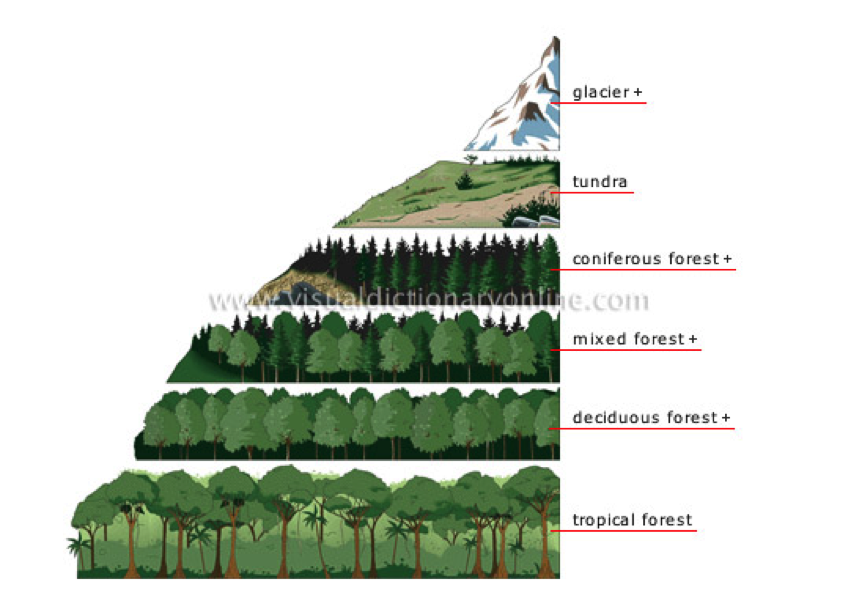
由于维度越高,温度越低,相应的地貌也发生了变化。
在高纬度high latitude地区有一种特别的地貌称之为tundra苔原,上面一层为活跃层upper/active layer,夏季会融化thaw/defrost/melt, 但是下面一层被称为permafrost 冻土,常年冰冻状态,因此大树的根系root system无法penetrate,因此只能长根系浅的矮小灌木 shrub/bush with shallow root system. Tundra这个地貌在新发布的TPO49中又有涉及,因此一定要能听辩!TPO49中还提到了北美Alaska阿拉斯加 有一种oriented thaw lake,就跟那个地区的sloping terrain倾斜的地貌 以及 冰楔 ice wedge有关。具体的原因不多加剧透,但是大家一定要对这些基本概念能够听辩。有意思的是,新航道出的托福听力教程有一篇talk就是关于这个oriented thaw lake (mp3-225 )的, 因此基础较差的同学强烈建议用教程拓宽学科知识&词汇听辩!
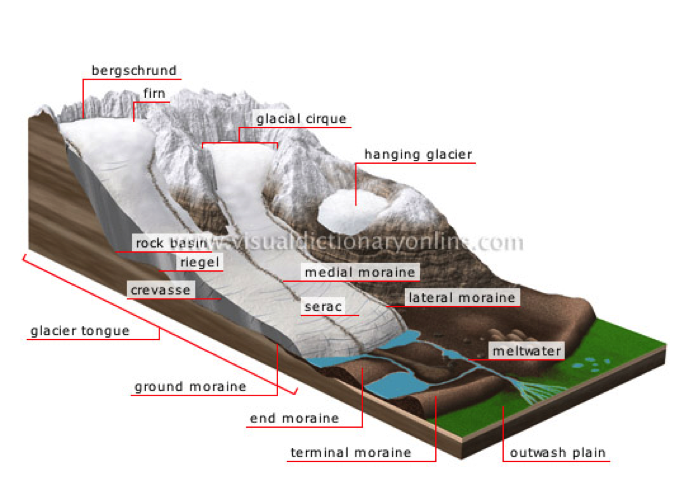
在极地地区 polar region,肯定少不了我们的glacier冰川。冰川的定义为:当某一区域降雪的堆积速度大于融化速度when more snowfalls during a year than melts,就因为自身重力逐渐形成了缓慢滑行的巨大冰块A glacier is an extremely large mass of ice which moves very slowly, often down a mountain valley due to its own gravity。积雪firn 是雪花snow flake 跟ice 冰之间的过渡状态,只要冰川处于降雪输入input from snow不小于融化output from melting输出的动态平衡状态,积雪就会因为自身的重力作用变成蓝色的冰interlocked crystals of blue glacial ice。
除了板块运动,当冰川滑行经过某一地带,巨大的能量可以碾碎甚至最坚硬的石头carving into even the hardest rock formation , 并把岩石碎片带到很远的地方, deposit rock debris in places far from its original location,也就是我们的冰碛石:冰川边缘泥土和松散岩石的聚集体moraine: accumulation of earth and loose rock that form at the edges of glaciers。因此冰川也可以塑造地形reshaping the landscape,而冰碛石就是冰川作用的证据glaciation。
冰川还是地球水循环hydrologic cycle的重要组成部分,其含水量仅次于海洋,事实上地球上大约80%的淡水fresh water都锁在冰川中。如果世界上全部的冰川都融化的话,海平面sea level将上升大约60米。
事实上,地球经历了多次大规模的冰期glacial period/ice age。冰期时,冰川大规模扩张或前进expand;间冰期时interglacial period,冰川消融后退retreat。一个冰期与相邻的间冰期两个对立而又互相转化的气候期,组合一个冰川周期 。A glacial period/ice age (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate between glacial periods. 最近的一次冰期大约15,000年前The last glacial period ended about 15,000 years ago. 全新世是最近的一次间冰期,并且一直持续到现在,很明显主要由人类活动释放大量温室气体导致The Holocene epoch is the current interglacial.
另外,但凡涉及到ice,希望大家记住两点基本的物理知识
1. ↑Pressure →melting point↓→ water at the basal part of the glacier melt as lubricant due to the pressure produced by the gravity of a huge glacier→friction 摩擦力↓→basal slip 基面滑移
2. The volume of ice > the volume of liquid water
冰的体积要比液态水大 (水在4 摄氏度的时候体积最小)
学科词汇
altitude/elevation海拔
glacial movement 冰川运动
basal slip基面滑移
friction摩擦力
moraine 冰碛石
bedrock 基岩;根底;基本原理
firn积雪: Accumulation of snow inside a cirque; compressed by its own weight, it is converted into ice and feeds the glacier.
glaciation 冰川作用
tundra 冻原,苔原
permafrost 冻土
upper/active layer活跃层 thaw/defrost/melt融化
sloping terrain倾斜的地貌
slump/slide/collapse 崩塌
penetrate穿透
ice wedge: An ice wedge is a crack in the ground formed by a narrow or thin piece of ice that measures up to 3–4 meters in length at ground level and extends downwards into the ground up to several meters. During the winter months, the water in the ground freezes and expands.
coniferous forest 针叶林
mixed forest混生林
deciduous forest落叶林
tropical rain forest 热带雨林
参见
TPO7L4 glacial movement
TPO15 Reading1 glacier formation
TPO19 Reading 3 discovering the ice age
TPO20L2 interglacial period
TPO9L2tundra
TPO49L1oriented thaw lake
托福听力教程MP3-225 oriented thaw lake
老托73 the Great Plain
英语高能高分·就上新航道
400-009-9696
推荐阅读
- 2019年4月13日托福写作考题解析
- 2019年3月31日托福写作考题解析
- 2019年3月30日托福写作考题解析
- 2019年4月托福独立口语考情分析
- 2019年3月30日托福独立口语参考答案
- 2016-2018年词汇题总结
- 2019年3月30日托福独立口语参考答案
【本文标签】:
【责任编辑】:武汉新航道小编 版权所有:转载请注明出处

